Nearly 60 mn people internally displaced worldwide in 2021

Conflicts and natural disasters forced tens of millions to flee within their own country last year, pushing the number of internally displaced people to a record high, monitors said Thursday.
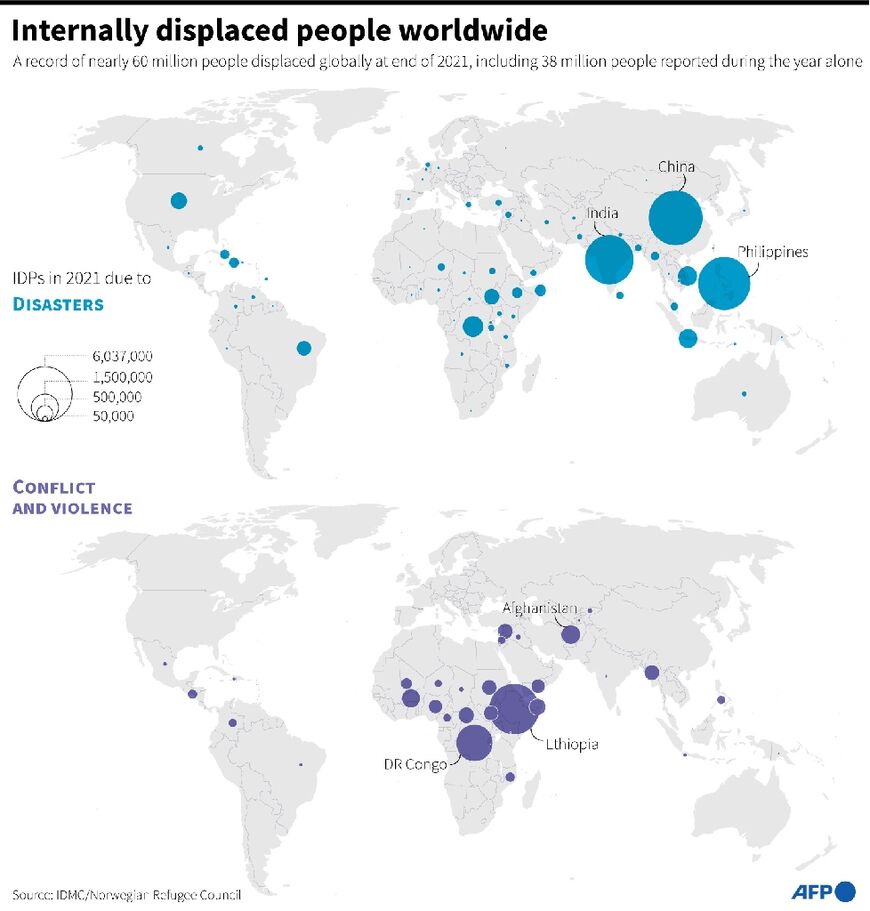
Some 59.1 million people were registered as internally displaced worldwide in 2021 -- an all-time record expected to be broken again this year amid mass displacement inside war-torn Ukraine.
Around 38 million new internal displacements were reported in 2021, with some people forced to flee multiple times during the year, according to a joint report by the Internal Displacement Monitoring Centre (IDMC) and the Norwegian Refugee Council (NRC).
That marks the second-highest annual number of new internal displacements in a decade after 2020, which saw record-breaking movement due to a string of natural disasters.
Last year, new internal displacements from conflict surged to 14.4 million -- marking a 50-percent jump from 2020 and more than doubling since 2012, the report showed.
- 'World is falling apart' -
And global internal displacement figures are only expected to grow this year, driven in particular by the war in Ukraine.
More than eight million people have already been displaced within the war-ravaged country since Russia's full-scale invasion began on February 24, in addition to the more than six million who have fled Ukraine as refugees.
"2022 is looking bleak," IDMC director Alexandra Bilak told reporters.
The record numbers seen in 2021, she said, marked "a tragic indictment really on the state of the world and on peace-building efforts in particular".
NRC chief Jan Egeland agreed, warning: "It has never been as bad as this."
"The world is falling apart," he told reporters.
"The situation today is phenomenally worse than even our record figure suggests."
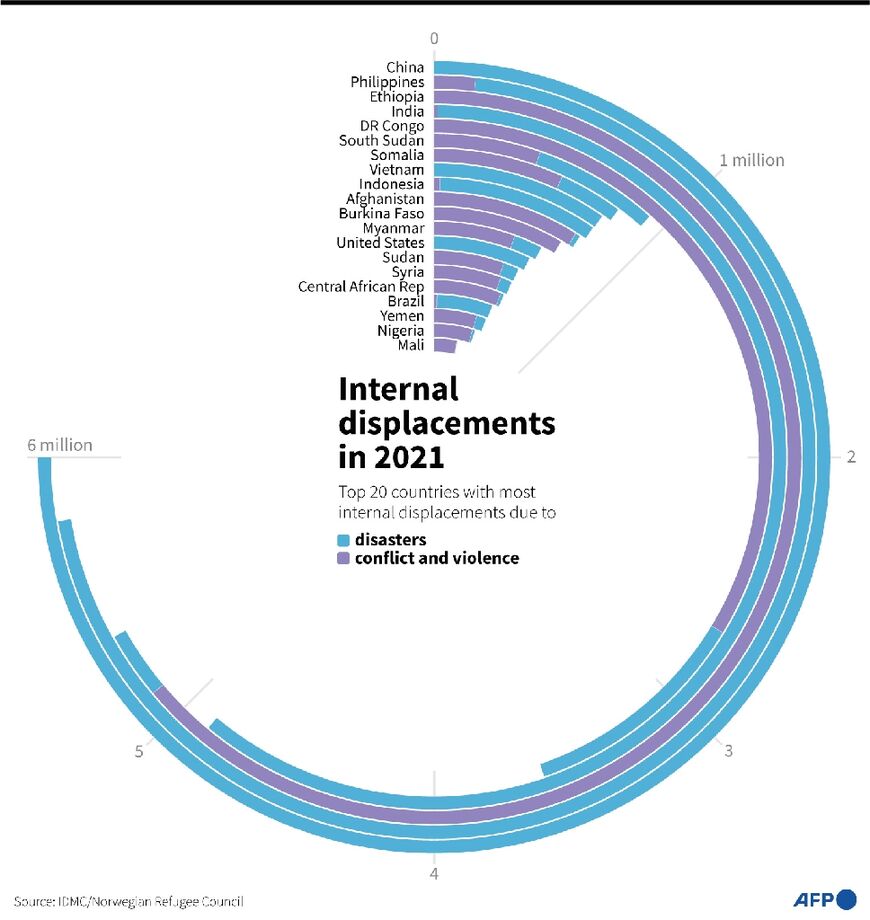
In 2021, sub-Saharan Africa counted the most internal movements, with more than five million displacements reported in Ethiopia alone, as the country grappled with the raging and expanding Tigray conflict and a devastating drought.
That marks the highest figure ever registered for a single country.
- 'Titanic shift' needed -
Unprecedented displacement numbers were also recorded last year in the Democratic Republic of Congo and Afghanistan, where the Taliban's return to power, along with drought, saw many flee their homes.
In Myanmar, where the military junta seized power in a February coup last year, displacement numbers also reached a record high, the report found.
The Middle East and North Africa region recorded its lowest number of new displacements in a decade, as the conflicts in Syria, Libya and Iraq de-escalated somewhat, but the overall number of displaced people in the region remained high.
Syria, where civil war has been raging for more than 11 years, still accounted for the world's highest number of people living in internal displacement due to conflict -- 6.7 million -- at the end of 2021.
That was followed by the DR Congo at 5.3 million, Colombia at 5.2 million, and Afghanistan and Yemen at 4.3 million.
Despite the hike in conflict-related displacement, natural disasters continued to account for most new internal displacement, spurring 23.7 million such movements in 2021.
A full 94 percent of those were attributed to weather and climate-related disasters, like cyclones, monsoon rains, floods and droughts.
Experts say that climate change is increasing the intensity and frequency of such extreme weather events.
China, the Philippines and India were hardest hit, together accounting for around 70 percent of all disaster-related displacements last year.
Increasingly, conflict and disasters collide, creating a "complex quagmire of problems", Egeland said, worsening risks and often forcing people to flee several times.
In places like Mozambique, Myanmar, Somalia and South Sudan, overlapping crises impact food security and heighten the vulnerabilities of millions.
"We need a titanic shift in thinking from world leaders on how to prevent and resolve conflicts to end this soaring human suffering," Egeland said.